What was claimed
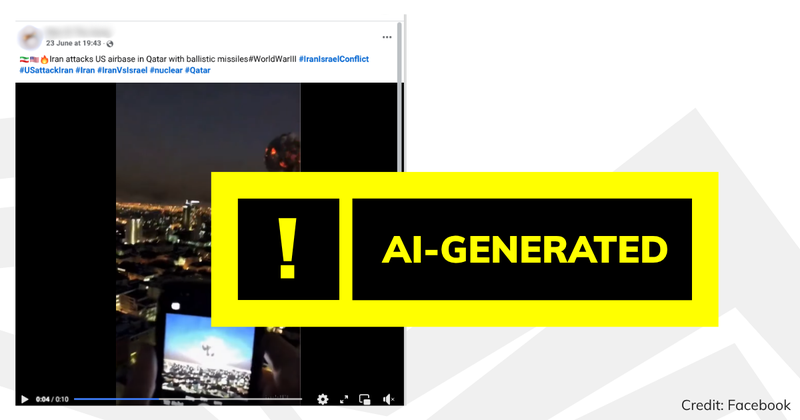
A video shows Iran attacking a US airbase in Qatar with ballistic missiles.
Our verdict
False. This video isn’t real and features OpenAI’s Sora watermark, indicating that it was generated using artificial intelligence.
What was claimed
A video shows Iran attacking a US airbase in Qatar with ballistic missiles.
Our verdict
False. This video isn’t real and features OpenAI’s Sora watermark, indicating that it was generated using artificial intelligence.
A video is being shared online with claims it shows Iran’s attack on a US airbase in Qatar—but it isn’t real, and was generated with artificial intelligence (AI).
The footage shows several explosions and large clouds of smoke over a city at night as a person films on their phone, and has been shared with the caption “Iran attacks US airbase in Qatar with ballistic missiles”.
While it is true that Iran launched missiles at a US military base in Qatar on 23 June, the video being shared isn’t real.
A white watermark that looks like a waveform that transforms into OpenAI’s logo can be seen in the bottom-right corner of the clip. This is a Sora watermark, which is an AI-model developed by OpenAI that creates videos from text instructions.
Experts such as James O’Brien, a professor of computer science at the University of California, Berkeley, also told fact checkers at Reuters that the cleanly defined and “inexplicably well lit” smoke was a telltale sign the video was artificially or computer-generated. He also noted the lack of shockwave after the explosions.
Reports about the attacks on 23 June often included eyewitnesses hearing loud bangs in the sky above the Qatari capital, Doha, and genuine videos do show bright flashes in the sky as air defence systems intercepted most of the missiles. But Full Fact could not find any evidence of footage resembling the dramatic scene in the viral video.
Join 73,000 newsletter subscribers who trust us to check the facts
Sign up to get weekly updates on politics, immigration, health and more.
Subscribe to weekly email newsletters from Full Fact for updates on politics, immigration, health and more. Our fact checks are free to read but not to produce, so you will also get occasional emails about fundraising and other ways you can help. You can unsubscribe at any time. For more information about how we use your data see our Privacy Policy.
Qatar reported that no one was killed or injured in the attack.
Since the recent conflict in the Middle East began, Full Fact has seen related misinformation circulating widely on social media. Before sharing content that you see online, consider whether it comes from a trustworthy and verifiable source. Our guides to spotting misleading images and videos can help you do this.
This article is part of our work fact checking potentially false pictures, videos and stories on Facebook. You can read more about this—and find out how to report Facebook content—here. For the purposes of that scheme, we’ve rated this claim as false because the video isn’t real and was generated using artificial intelligence.
Full Fact fights for good, reliable information in the media, online, and in politics.
Bad information ruins lives. It promotes hate, damages people’s health, and hurts democracy. You deserve better.
Subscribe to weekly email newsletters from Full Fact for updates on politics, immigration, health and more. Our fact checks are free to read but not to produce, so you will also get occasional emails about fundraising and other ways you can help. You can unsubscribe at any time. For more information about how we use your data see our Privacy Policy.